Research & Publications
Endoscopic Versus Open Cranial Reconstruction Surgery for Anterior Craniosynostosis: Experience from South-East Asia
Mendonca DA, Gopal S, Gujjalanavar R, Vybhav D, Sunil HR, Ramamurthy V. Endoscopic versus open cranial reconstruction surgery for craniosynostosis; experience from South East Asia. FACE 2020, 1 (2), 105-113.
Nitroglycerin patch use in digital ischemia secondary to sepsis
Plasticos spreads it's wings. First stop Australia.We are proud to announce that we have collaborated with MAFAC(Melbourne Advanced Facial Anatomy Course Course)
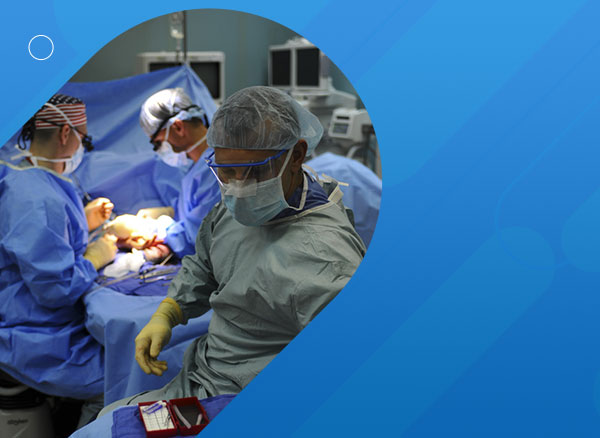
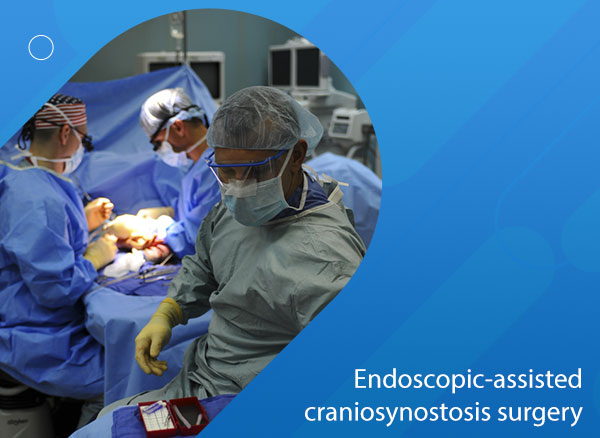
Endoscopic-assisted craniosynostosis surgery: First case series in India
Craniosynostosis is a congenital pathological condition resulting from premature fusion of sutures of the cranial vault and leads to an abnormal head shape with a significant risk of raised intracranial pressure.
Can 3D Printing Technology Offer Economic Advantages for Disadvantaged Patients in Resource Poor Countries who Require Complex Craniofacial Surgery?
There is conflicting evidence on the role of raised inflammatory markers in acute ureteric colic with regards to need for intervention after discharge with conservative management.
The Journal of the American Society of Maxillofacial Surgeons
There is a severe lack of formally trained craniofacial surgeons in India, a country with an approximate population of 1.3 billion. Most craniofacial surgery centres are located in teaching medical hospitals/institutions.
3D printing technology applied in complex craniofacial deformity surgery
Three-dimensional (3D) printing (additive manufacturing, rapid prototyping) is a technology that has attracted the attention of craniofacial surgeons to gain perfection in analysis, planning and execution of complex surgical challenges.
Long-Term Incisal Relationships After Palatoplasty in Patients With Isolated Cleft Palate
Various palatoplasty techniques have limited incisions in the hard palate due to concerns that these incisions may limit maxillary growth. There is little convincing long-term evidence to support this.
Fronto-orbital advancement
Craniosynostosis is a pathologic condition resulting from the premature fusion of cranial vault sutures, resulting in craniofacial deformities. Anterior craniosynostosis can involve a combination of metopic/unicoronal or bicoronal sutures.
Pierre Robin Sequence
Pierre Robin sequence (PRS) is classically described as a triad of micrognathia, glossoptosis, and airway obstruction. Infants frequently present at birth with a hypoplastic mandible and difficulty breathing. The smaller mandible displaces the tongue posteriorly, resulting in obstruction of the airway.